Heat Transfer Through Conduction

Heat Transfer Through Conduction
Transfer of heat:
Heat is transferred by conduction, convection and radiation.
Conduction -
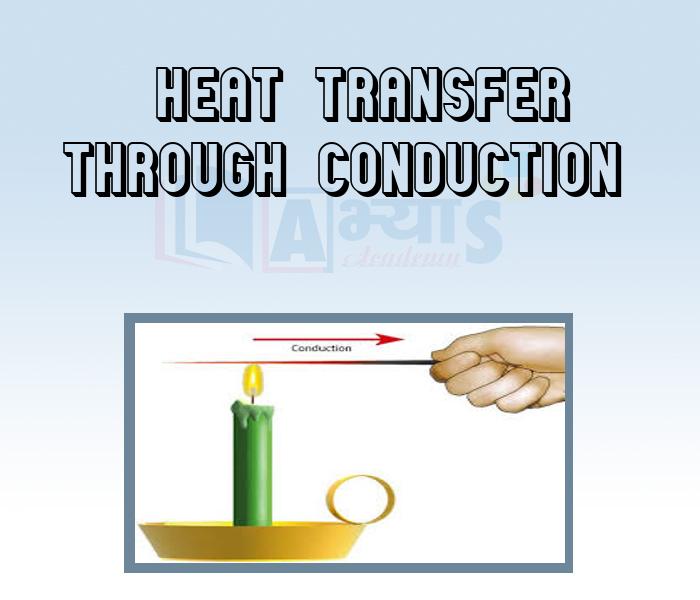
Transfer of heat from one particle to the adjacent particle is known as conduction of heat. In solids, heat is transferred by the process of conduction. In this process, the transfer of heat takes place through adjacent molecules.
Example: When one end of an iron rod is put over flame then part which is nearer to the flame is heated first and heat is gradually transferred to the other end of the rod. This happens because particles of iron rod which are nearer to the flame receive the heat and transfers this to the adjacent particles. Subsequently, the adjacent particles transfer the heat to the next adjacent particles. This process continues and heat reaches to the other end of the rod. Thus, heat transfer in solid takes place through conduction.
Conductor and Insulator:
Materials which allow heat to pass through it are called conductor or good conductor of heat, such as iron, copper, aluminium, etc. All metals are good conductors of heat. Since, mercury is a metal and found in liquid state at room temperature, that’s why it is used in thermometer.
Since metals are the good conductor of heat that’s why kitchen utensils are made of metals or alloys of metals.
Materials which do not allow heat to pass through them are called bad conductor or poor conductor of heat. They are also called insulators. Example: rubber, wood, plastic, etc. This is the cause that handles of frying pan or other kitchen utensils are made of plastic.
Application Of Conduction And Insulators
Stainless steel pans are usually provied with copper bottoms. The reason for this could be that | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
An iron ball at | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Materials which do not allow heat to pass through them are called ___________________ . | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
My experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.
